What is latency? Let’s deep dive & understand possible ways to optimise it.
Everything you need to know about latency.
Hi 👋,
Latency is yet another, a very important topic when we talk about backend engineering or networking. In this article, we will be discussing latency, it's importance and ways to optimise it in order to improve application performance.
Table of Contents
- What is latency?
- Why is it important?
- What causes latency?
- How to measure latency?
- How to optimise the latency?
- Conclusion
1. What is latency?
Latency is the total time between a client’s action and the server’s response to that action. It’s simply a round trip time between browser & server.
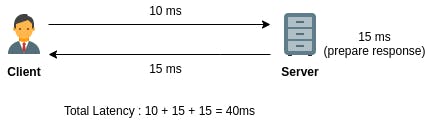
Network latency is measured in milliseconds (ms).
2. Why is it important?
Latency is directly related to the performance of the application. High latency means a slow network and no one likes to be on a slow website. At a large scale, latency plays a very critical role.
Let’s understand with a simple example by emulating a GET request in a browser.
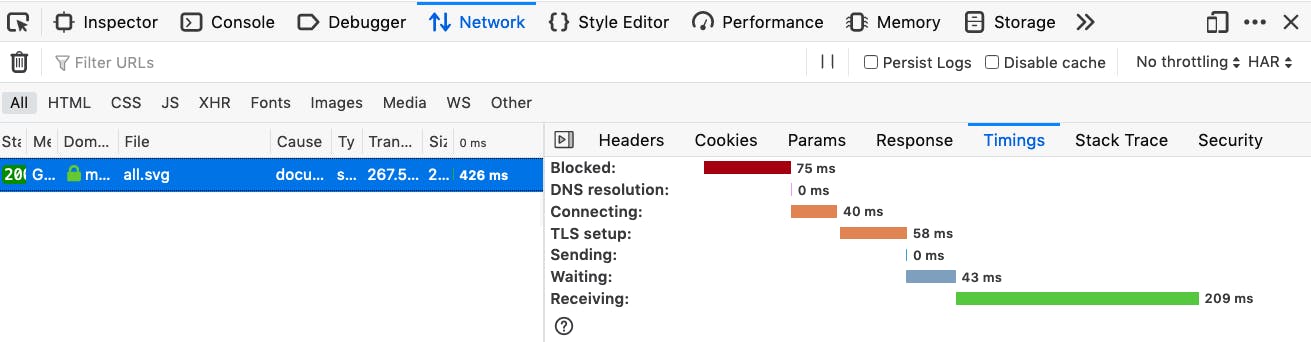
Blocking : The time for which request was in queue. (A chrome browser can only make at max 6 HTTP request at a time to the server)
DNS Resolution : Time taken in DNS lookup
Connecting : Time taken in a TCP handshake
TLS Setup : Time taken in establishing a secure TLS connection
Sending : Time taken to send the HTTP request to the server
Waiting : Time taken by the server to prepare the response
Receiving : Time taken to receive the response from server
For the very first request, for the first 14KB data, latency is longer due to DNS lookup, a TCP handshake and the secure TLS negotiation.
3. What causes latency?
Latency plays a vital role in system performance. It depends on various factors -
- Distance
One of the principal causes of network latency is distance between client (who is making request) and the server (responding to the request).
For example - Suppose, my website (pankajtanwar.in) is hosted in a data center in Delhi. So, for a user accessing from Jaipur (~200KM from Delhi), it is likely to respond within 20-30ms but for a user accessing from New York (~11000 KM from Delhi), it might face a latency close to 70ms.
- Transmission Medium
The type of transmission medium being used for data packet transmission also impacts the latency. Modern optic fiber is ~200 times faster than old copper cable-based networks.
- Multiple Routers
We should not ignore the fact that routers play a very important role in latency. Routers take some time and analyse the headers of each data package passing thought, which adds to network latency.
- Poorly optimized server
Several factors on the backend server, such as slow database queries, low memory space, slow data processing and un-optimized code also impacts the latency.
4. How to measure latency?
There are several standard metrics to measure latency.
- Time to First Byte (TTFB)
This is one of the widely accepted matrices to measure latency. As the name itself explains, TTFB is the time (in milliseconds) for a browser to receive the first byte of response from the server.
- Ping
Ping is the most common utility to measure latency. It sends a 32 bytes packet to the server & measures the time it took to reach the destination and come back with response to the client.
- Round Trip Time (RTT)
It’s a pretty common and simple matrix. It is the total time taken by the data packet, travelling from source to the destination and back.
5. How to optimize the latency?
In terms of application performance optimization, It is very important to reduce the causes of high latency. Here are major methods, which can help us reduce the latency.
- CDN
Using CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a major step towards reducing the latency. CDN, caches content, serves it from the nearest data centre & provides an efficient path for data packets to travel on, which drastically reduces the round trip time and so latency.
- HTTP/2
HTTP/2 is a highly efficient protocol which reduces the latency by enabling parallelised data transfers, response multiplexing, requests prioritisation, minimised protocol overhead by efficient compression of HTTP headers, reduced round trips and many more.
- Client Side Caching
Browsers can cache some of the resources which reduces the calls to the server and improves the latency.
- Server Side Optimisations
Server side optimisations such as less disk I/O, caching, efficient algorithms, smart database layer & asynchronous programming can help in optimising the latency.
6. Conclusion
Latency might seem a very simple concept but it plays a very crucial role when we build high scale systems like trading or gaming software. For such systems, even a double digit millisecond latency affects the performance.
In the next article, we will discuss how to system design a real time multiplayer game counter-strike (CS-Go) which is highly sensitive to latency (or ‘lag’).
References
