Twitter Usage Statistics
- 500MN tweets per day
- ~7000 tweets per second
- 8,00,000+ Queries per second
Typical Database server config at Twitter
HP DL380, 72GB RAM, 24 disk RAID10
Twitter's Old Tweet store
They were using MySQL.
- Pretty fast
- Very robust data storage data layer
- replication works pretty well
- easy to use and setup
The old way of storing tweets at Twitter was using temporal sharding.
- Temporal sharding means tweets from the same date range are stored together on the same shard
- They soon realized the problem. Tweets filled up one machine, then a second, then third and they end up filling up one machine after another.
The major issue
- Load balancing : Old machines didn't get any traffic because on twitter, people are interested in what's happening now.
- Expensive & complicated : It was too expensive & complicated for the DBA (Database Administrator) team at twitter to setup a whole new cluster every three weeks as tweets were filling up one machine every three weeks.
Twitter's new tweet store
Twitter built a brilliant data storage framework, Gizzard for creating distributed datastores.
In simple words, Gizzard is a middleware networking service that manages partitioning data across arbitrary backend datastores (e.g., SQL databases, Lucene, Redis or any datastorage backend we can imagine). The partitioning rules are stored in a forwarding table that maps key ranges to partitions. Each partition manages its own replication through a declarative replication tree.
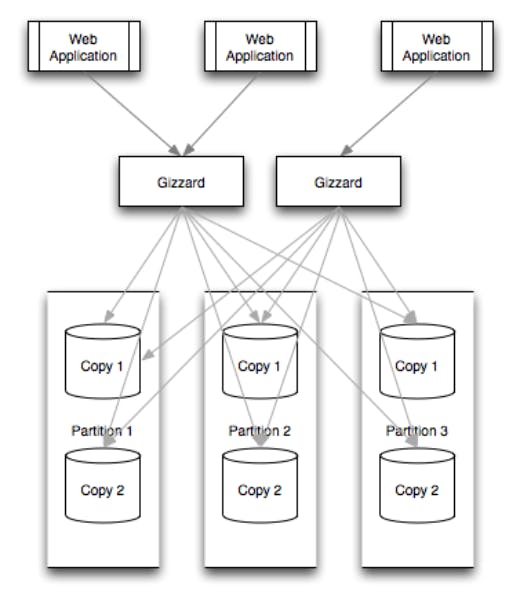
Basically, Gizzard sits “in the middle” between clients (typically, web front-ends like PHP and Ruby on Rails applications) and the many partitions and replicas of data. Sitting in the middle, all data querying and manipulation flow through Gizzard.
The New System now at Twitter
When ever we tweet, its stored in an internal system "T-bird" which is built on the top of Gizzard. Secondary indexes are stored in "T-flock" (Gizzard based). Unique Ids are generated using "Snowflake". FlockDB is used for ID to ID mapping. It basically stores the relationships between IDs.
Gizzard implements a tweet store that isn't perfect in the sense of load balancing, but it allows:
Growing slowly - No need to worry about a machine getting filled up and creating a whole new cluster at an exact time
Some Rest for DBA team - Now, DBA team don't need to make decisions so frequently.
When and which DB twitter uses?
MySQL - MySQL doesnot work for ID generation and graph storage. They use MySQL for smaller dataset of <= 1.5TB and as a permanent backing store for large datasets
Cassandra - Its used for high velocity writes and medium-low velocity reads. Another advantages are easy cluster expansion,can run on cheap and simple hardware than MySQL & schema less design is a major plus.
Hadoop - Twitter uses hadoop internally for unstructured and large dataset (~100s of billions of rows eg. http logs). The major advantage is its massive horizontally scalability & redundancy.
Vertica - It is being used for analytics and large aggregations and joins so they don't have to write MapReduce jobs.
Thanks for reading.
Source : Jeremy Cole's (Database Architect @ Twitter) talk at O'Reilly MySQL conference
About me : pankajtanwar.in
